The automotive industry is undergoing a seismic shift as advanced electric drivetrains take center stage. These innovative systems not only enhance vehicle performance but also pave the way for a sustainable future. As manufacturers and consumers alike embrace electric mobility, understanding the intricacies of these drivetrains becomes essential.
Advanced electric drivetrains combine cutting-edge technology with efficiency, offering significant advantages over traditional combustion engines. From improved torque delivery to regenerative braking, these systems are designed to maximize energy use and minimize environmental impact. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, exploring the latest advancements in drivetrains reveals the exciting possibilities ahead for both the industry and the planet.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Advanced Electric Drivetrains
Advanced electric drivetrains consist of several key components that enhance efficiency and performance. These systems typically include electric motors, battery packs, power electronics, and associated control systems.
Electric Motors
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. They provide instant torque, resulting in quicker acceleration compared to combustion engines. Various motor types, such as permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) and induction motors, offer different performance characteristics. PMSMs exhibit high efficiency and power density, making them popular in electric vehicles (EVs).
Battery Packs
Battery packs store energy for electric drivetrains. Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their high energy density and efficiency. Innovations, like solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries, promise increased energy capacity and reduced charging times. Effective thermal management systems also enhance battery longevity and performance.
Power Electronics
Power electronics convert and control electrical energy flow between the battery and electric motor. They improve system efficiency, enabling features such as regenerative braking, which recovers energy during deceleration. Inverters play a crucial role in this process, managing the transition between AC and DC currents.
Control Systems
Control systems optimize the performance of electric drivetrains. Advanced algorithms analyze data from sensors and adjust power distribution for various driving conditions. These systems enhance vehicle stability, safety, and responsiveness, contributing to an improved driving experience.
Benefits of Advanced Electric Drivetrains
Advanced electric drivetrains offer numerous benefits over traditional combustion engines. They provide reduced emissions, lower operational costs, and enhanced vehicle performance. Furthermore, they support the growing trend toward sustainable transportation, aligning with global environmental goals. The shift toward electrification reflects the industry’s commitment to innovation and sustainability.
Key Components of Advanced Electric Drivetrains
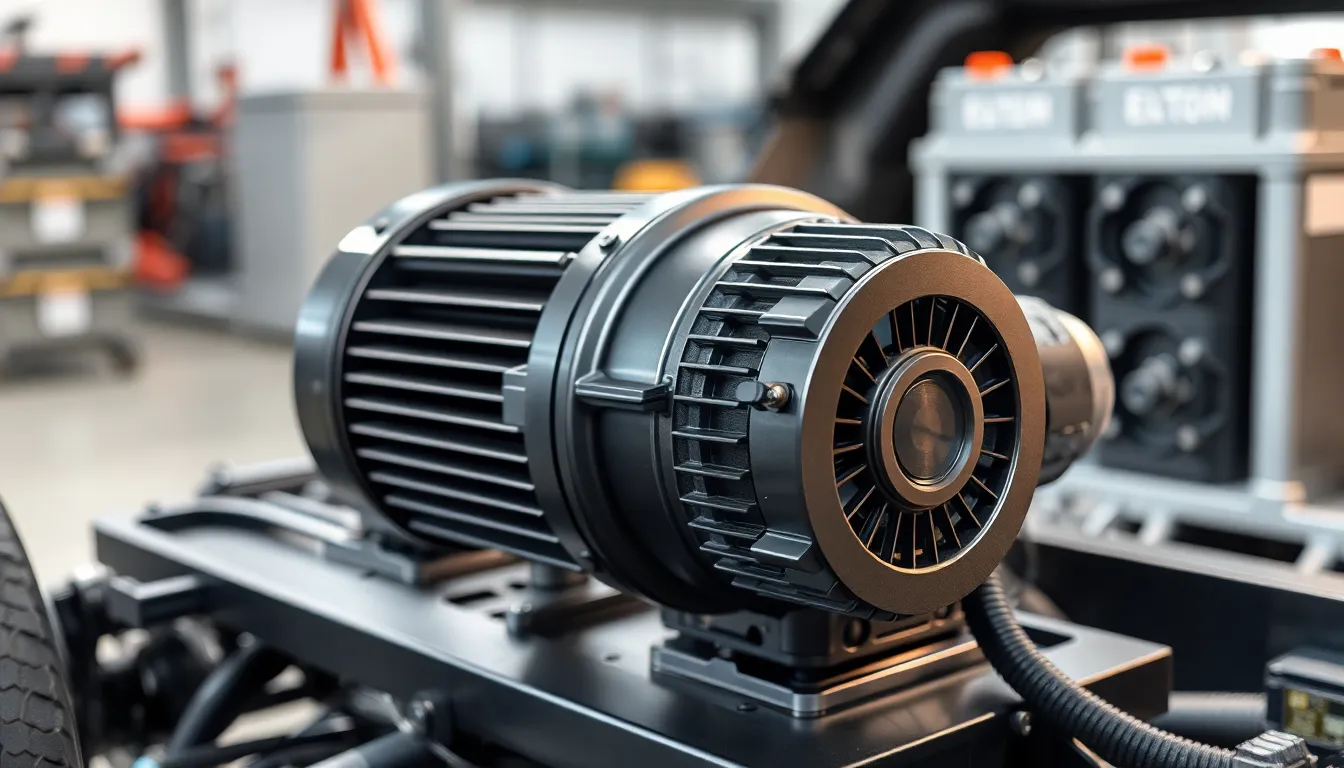
Advanced electric drivetrains consist of several critical components that work together to enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. Each component plays a significant role in delivering the advantages associated with electric mobility.
Electric Motors
Electric motors serve as the core of advanced drivetrains, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. These motors provide instant torque, enabling rapid acceleration and responsive handling. Most electric vehicles utilize permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) due to their high efficiency and compact design. Innovations in motor design, such as improved cooling systems and higher power density, further enhance performance and thermal management.
Power Electronics
Power electronics control the flow of electrical energy within the drivetrain. These components include inverters and converters, which manage the power supplied to the electric motor and regulate energy flowing to and from the battery. Advanced algorithms in power electronics facilitate regenerative braking, allowing energy recovery during deceleration. Efficient power electronics minimize energy losses, significantly enhancing overall system efficiency.
Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems primarily consist of lithium-ion battery packs, which provide the electrical energy required for operation. These battery packs are designed for high energy density, enabling longer driving ranges. Emerging technologies, such as solid-state and lithium-sulfur batteries, promise higher capacity and faster charging times. Additionally, advanced thermal management systems within battery packs ensure optimal performance and longevity by regulating temperature during operation.
Types of Advanced Electric Drivetrains
Advanced electric drivetrains come in several configurations, each contributing to vehicle efficiency and performance. Key types include series hybrid, parallel hybrid, and fully electric drivetrains.
Series Hybrid Drivetrains
Series hybrid drivetrains utilize an electric motor as the primary source of propulsion. In this system, a combustion engine functions solely as a generator, charging the battery while not directly driving the wheels. Electric motors provide torque and acceleration, allowing smoother operation. This configuration optimizes fuel efficiency, especially in urban settings, where stop-and-go driving affects traditional engines adversely.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved fuel efficiency | Limited top speed |
| Reduced engine noise | Increased weight due to extra components |
| Enhanced acceleration | Complex energy management |
Parallel Hybrid Drivetrains
Parallel hybrid drivetrains employ both a combustion engine and an electric motor to power the vehicle. Both sources can work simultaneously or independently based on driving conditions. This setup allows for optimal performance and efficiency, as the system can switch between power sources for acceleration or fuel economy. The versatility makes it suitable for diverse driving scenarios, from urban commutes to highway trips.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Greater power output | Increased complexity of the system |
| Better performance under load | More maintenance needs |
| Flexible driving modes | Potential for higher emissions |
Fully Electric Drivetrains
Fully electric drivetrains rely exclusively on electric motors for propulsion. These systems utilize battery packs to store energy and deliver power to the wheels. Electric drivetrains excel in efficiency and torque delivery, offering swift acceleration and quiet operation. Recharge times are decreasing with advancements in charging technology. Regenerative braking systems capture energy during deceleration, improving range.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Zero emissions | Limited range depending on battery capacity |
| Lower operational costs | Charging infrastructure needs improvement |
| Quick acceleration | Longer refill times compared to refueling |
Benefits of Advanced Electric Drivetrains
Advanced electric drivetrains offer numerous advantages over traditional combustion engines. They enhance efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve overall vehicle performance.
Increased Efficiency
Electric drivetrains achieve higher efficiency through their design and operation. Electric motors convert more than 90% of electrical energy into movement, significantly surpassing the efficiency of internal combustion engines, which typically operate at about 20-30% efficiency. Regenerative braking systems capture energy during braking, redirecting it to recharge the batteries. This process minimizes energy loss and maximizes energy utilization, resulting in more miles per charge.
Reduced Emissions
Advanced electric drivetrains contribute to environmental sustainability by producing zero tailpipe emissions. Fully electric vehicles, using these drivetrains, eliminate pollutants like carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. The integration of renewable energy sources in electric power generation further reduces the overall carbon footprint. As the grid becomes cleaner, the lifecycle emissions of electric vehicles decrease, aligning with global targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Enhanced Performance
Electric drivetrains deliver superior performance thanks to their instant torque capabilities. Electric motors provide immediate power delivery, resulting in quicker accelerations compared to conventional vehicles. This characteristic allows for a more responsive driving experience. Additionally, advancements in drivetrain technology, such as improved thermal management and lighter battery materials, enhance performance metrics across various driving conditions. These features not only improve acceleration but also ensure better handling and overall vehicle dynamics.
Challenges and Future Trends
Advanced electric drivetrains face several technological and market challenges that could impact their growth and adoption. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for anticipating future trends in the automotive industry.
Technological Barriers
Technological barriers inhibit the widespread adoption of advanced electric drivetrains. Limited battery technology restricts energy density and charging speed. Current lithium-ion batteries might not meet the demands for increased range and quick recharging, leading to the exploration of alternatives like solid-state and lithium-sulfur batteries. Manufacturers face challenges in ensuring these newer technologies are viable for mass production.
Moreover, electric drivetrains rely on sophisticated power electronics for efficient energy management. Current systems must evolve to handle increased loads and improve thermal management, as overheating can damage components and reduce efficiency. Algorithms for energy management require further refinement to maximize regenerative braking and optimize overall performance. Additionally, the complexity of integrating these systems complicates manufacturing processes and drives up costs.
Market Adoption
Market adoption of advanced electric drivetrains is influenced by several factors. Consumer concerns about range anxiety impede sales. Many potential buyers hesitate to switch to electric vehicles without access to an extensive charging infrastructure. Expanding charging networks and developing fast-charging solutions are critical to overcoming this barrier.
Additionally, the high upfront cost of electric vehicles deters potential customers. Automakers must streamline production processes, reduce component costs, and leverage economies of scale to lower prices. Government incentives and subsidies can boost adoption rates, but policy consistency remains vital for sustained growth.
Moreover, consumers may need education about the benefits and functionality of electric vehicles. Increasing awareness of sustainability and performance advantages can drive demand. Partnerships between manufacturers and charging station providers can create a more comprehensive electric vehicle ecosystem, addressing consumer needs for convenience and accessibility.
The evolution of advanced electric drivetrains marks a pivotal moment in the automotive landscape. By enhancing vehicle efficiency and performance while promoting sustainability, these systems are reshaping how people think about transportation.
Innovations in electric motors and energy storage solutions are driving the industry forward, offering exciting possibilities for the future. As challenges like battery technology and charging infrastructure are addressed, the adoption of electric drivetrains is set to accelerate.
With growing consumer awareness and a commitment to reducing emissions, the shift towards electric vehicles is not just a trend but a necessary evolution. The road ahead promises a cleaner and more efficient driving experience for everyone.



